Fifteen partners participated in this benchmarking, twelve companies, most of them industrial, plus the Technological Institute of Aragón and the two Aragonese universities; obtaining data both quantitatively, on costs, and on a qualitative level, on trends, projects, good practices and opportunities for improvement. Detailed figures have been compiled on all expenses and investments in the ICT area, including personnel expenses, fixed, mobile and data communications, computer equipment, investments in licenses and application development, as well as miscellaneous expenses. As it is a second edition of the benchmarking carried out in 2005, it is possible to compare the evolution of the ratios over these eight years.
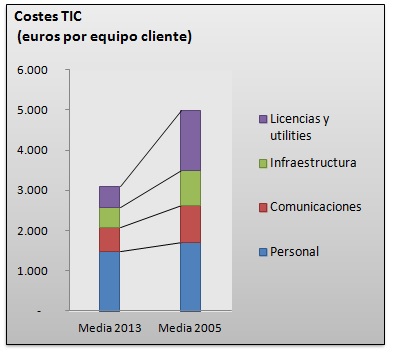
According to this study, the average annual ICT cost per IT device for participating IDiA partners is € 3,784, 32% less than in 2005, taking into account the revalued amounts to obtain equivalent prices. We have divided this cost into four large blocks: personnel expenses, communications, infrastructures and licenses.
- Personnel expenditure represents 49%, € 1,868, corresponds to expenses of internal or external personnel. It is the only ratio that goes up compared to 2005, 9% more.
- Communications represent a total of 19%, € 737, down 24% compared to 2005, although the detail of this item stands out for the decrease in telephony by 24% and the significant increase in data communication, increasing by 28%. %.
- Infrastructure is € 619, 16% of the total. It is down 41% compared to 2005, consistent with the cheapening of many teams.
- Licenses and other expenses weigh 15%, € 561 on the total. Notable decline driven by the improvement in printing costs.
The obtained relevant and detailed information, allows participants to compare and identify key references for critical decision making: where do the ICT investments of the companies studied go?
In this continuous process, multiple opportunities for improvement are identified, some of them to be explored in work groups share experiences with and agree in some cases actions in terms of purchase agreements, choice of mobile operating systems (Android, iOS or Windows), policies of print control, desktop virtualization, the alternative between acquiring standard packages or developing applications with their own means, as well as the implementation of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), which enables the use of private devices in business environments, among others.